Musculoskeletal Imaging & Its Role in Sports Performance
Both elite athletes and recreational sports enthusiasts experience physical stress each time they participate in sports activities, whether on the court, field, or track. While physical exertion enhances cardiovascular function, strengthens muscles, and promotes longevity, the repetitive movements common in many sports can negatively impact specific regions of the body over time.
Muscle strains, tendon and ligament injuries, and repetitive stress injuries are risks encountered in the pursuit of physical fitness and athletic achievement. However, these risks can be significantly mitigated or even eliminated through advanced musculoskeletal imaging techniques. This type of imaging employs detailed diagnostic methods to detect and assess sports-related injuries, providing crucial insights into the impact of physical stress on the body.
Musculoskeletal radiology is essential not only for professional athletes but also for recreational participants.
The Importance of Diagnostic Imaging in Sports Medicine
Diagnostic imaging in sports medicine is crucial for the early detection of issues, often identified at the onset of minor discomfort or persistent pain. Early diagnosis is vital to prevent minor irritations from escalating into severe injuries. This allows for the accurate determination of the implications of continued activity and the development of a tailored recovery plan to prevent the exacerbation of injuries.
Diagnostic imaging fundamentally involves creating detailed images of the body’s internal structures, allowing for precise analysis of sports-related damage. This critical step aids elite athletes in planning their return to activity.
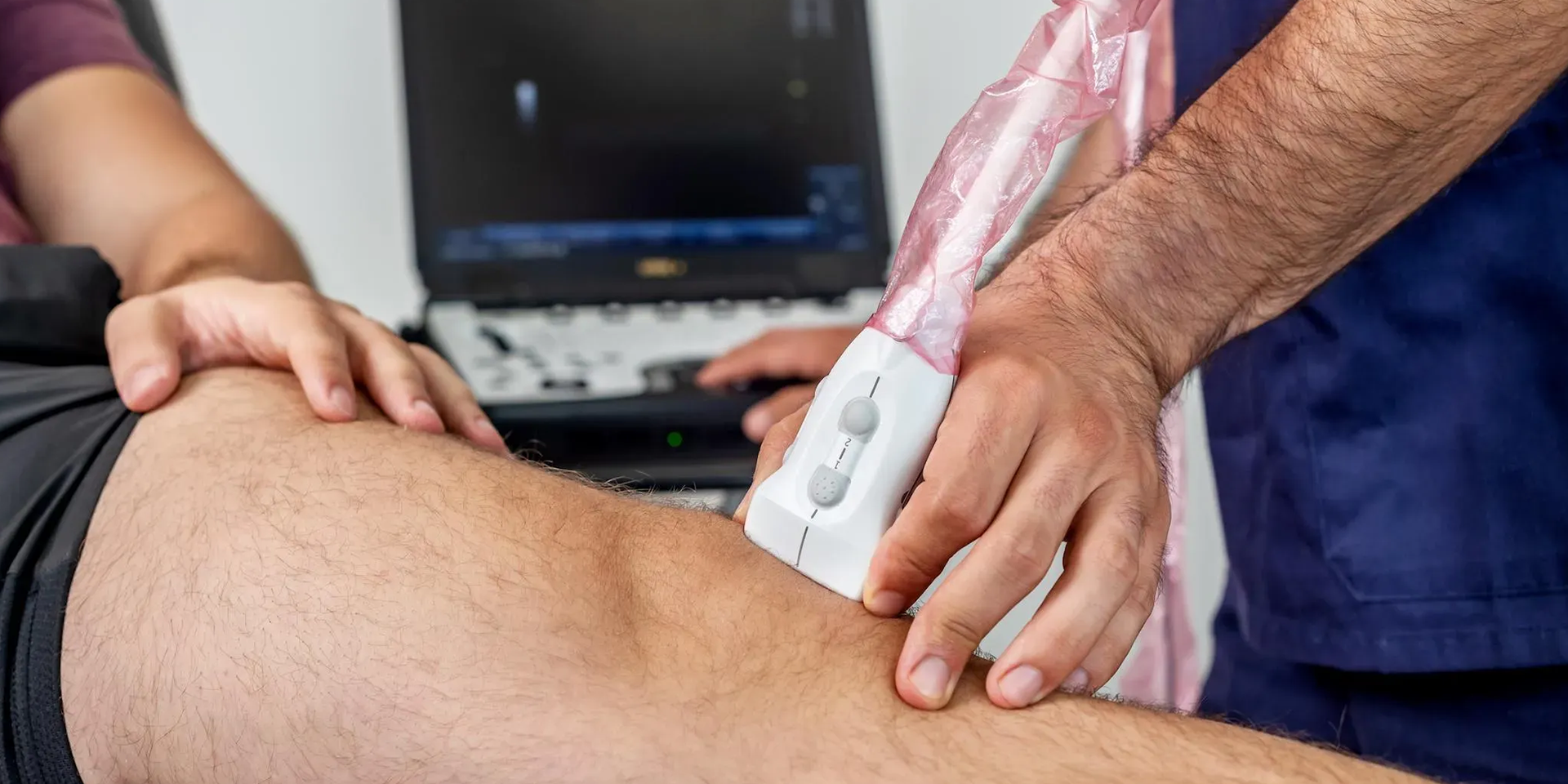
Imaging Techniques for Musculoskeletal Abnormalities and Injuries
Common imaging techniques include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound scans, X-rays. These modalities are highly effective in detecting and diagnosing injuries to both muscles and bones.
By accurately determining the extent and severity of an injury, these techniques inform treatment plans and guide rehabilitation programs. Each method has its strengths and limitations, and the choice of modality depends on the specific injury and needs of the patient. For instance, X-rays are optimal for identifying bone fractures, while diagnostic ultrasound excels in detecting damage to tendons, ligaments, muscles, and nerves. CT scans, reserved for more complex injuries, can detect damage to both muscle and bone, such as compound fractures or deep tissue injuries.
Combining these techniques creates a comprehensive diagnostic toolkit, playing a significant role in the evolution of modern sports medicine. Together with therapeutic treatments, sports medicine physicians can develop complete treatment and rehabilitation plans.